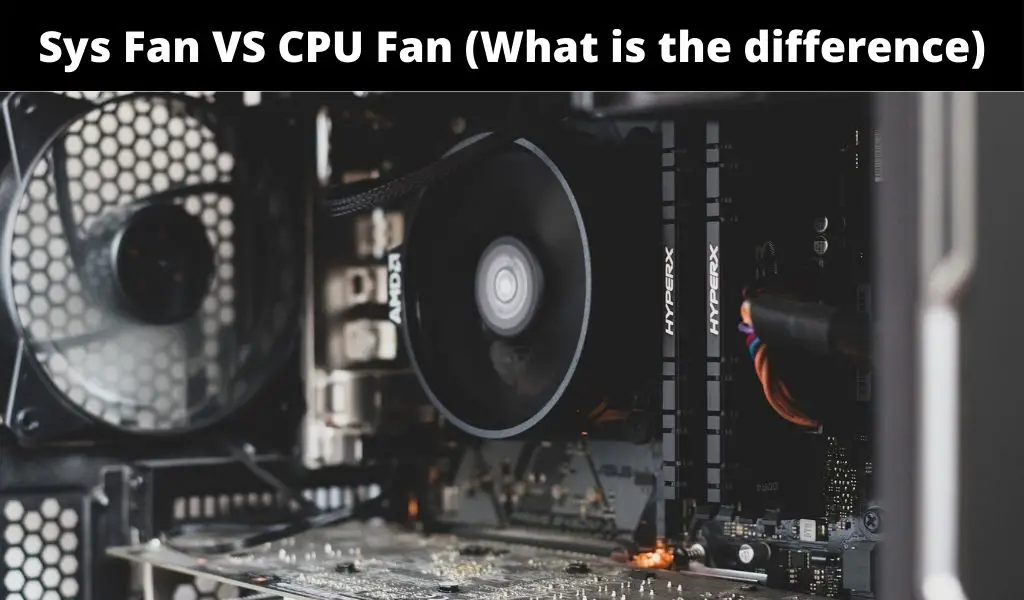
It can be confusing to understand the components as well as the moving parts of a computer, especially if you are trying to build one on your own. Whether it is the CPU fan or a sys fan, you have to know what function each one serves, which is why the following lines show the difference between them.
How is Sys Fan different from CPU Fan?
When it comes to sys fan VS CPU fan, the main difference lies in their functions, in which a system fan works to ventilate the machine’s case or chassis while the CPU fan keeps the CPU cool. Understanding this difference can help you install proper ventilation for your PC.
Sys Fan VS CPU Fan
Based on their functions, sys fans and CPU fans are placed accordingly. Located in the machine’s case, sys fans allow cool air to enter while giving off hot air. The CPU fans, on the other hand, are placed at the top part of the processor to prevent the CPU from getting overheated by blowing away the hot air from the CPU.
Another major difference between these two fans is their fan headers. However, both the System fan header and CPU fan headers are situated on the motherboard. Let’s understand each of these fan types in detail here.
Sys Fan
System fan or case fan works to ventilate air all through the computer case. If we look in detail, these fans have two separate functions- exhaust fans and intake fans.
The location of exhaust fans is either at the top or back part of the machine’s case, and they function to give off warm air that is built inside the computer’s case. Intake fans, on the other hand, are located either at the bottom or front part of the computer’s case, where they draw in cool air to keep the internal part of the case cool.
Also, there are specific standard-ATX tower cases that are equipped with fan sockets and vents for installing fans to directly cool the expansion cards and the motherboard’s components.
Again, there is a wide range of case fans in today’s market that feature LEDs for improving your machine’s aesthetic appeal.
Essentially, the sys fans work to provide proper airflow to the machine so that safe temperatures are maintained, which in turn, ensures that the machine’s performance is maintained.
Sys fans are available in numerous sizes, which include 40mm, 60mm, 80mm, 92mm, 120mm, 140mm, 200mm, and 220mm. The most-used size is 120mm because these fans are highly efficient in keeping a standard PC cool.
Headers for Sys fans
This type of header keeps the sys fans and motherboard connected. The header works to provide speed control, proper monitoring ability, and voltage control to the fans that stay connected (to the motherboard). In essence, the power of every fan installed on the machine should stay connected to the header of sys fans.
There can be several sys fan headers on a single motherboard, starting from 2 and moving on to 3 or even more. The average amperage of the sys fan header is similar to that of other fan headers, and it stands at 1 amp.
What you should ensure is that this amperage rating does not exceed 1 amp at all. Even if you set up a system to split the header (fan) with the help of a Y-headed splitter, the amperage of total fans secured to that single header must not go beyond 1 amp.
Ideally, the overall amperage of total fans secured to a single header (sys fan) must stay at approximately 0.75A (which is 75 percent of the overall amp rating of a header).
Types of Headers for system fan
Headers for sys fans come in two types- the 3 pin variety and the 4 pin variety. The 3 pin variety function for DC fans and the 4 pin headers find use in PWM fans. Both these types provide power and speed control and monitoring ability.
The 3 pin type header- These are used for DC fans. The DC fans, which have been in use for a long time, are less expensive and provide speed control that is not very impressive.
The 4 pin type header- These find use during the installation of PWM fans. The PWM fans are comparatively costlier than DC fans, provide better speed control, and also generate noise that is lower than DC fans.
CPU Fan
The Central Processing Unit or CPU is considered to be a computer’s brain, which functions to carry out all the tasks assigned to the machine. This is the main reason why a machine is equipped with a separate CPU fan that is dedicated to keeping the CPU from getting overheated. If the CPU is not kept cool, it would result in overheating in seconds, destroying your entire machine in no time.
The heatsink that remains secured to a CPU works simultaneously with the fan of the CPU to ensure proper cooling and ventilation. This heatsink is a component that is made from metal, which sits on the machine’s processor. The main function of this heatsink is drawing away from the heat from the processor’s chip onto the fin-like, aluminum construction of this component.
The fan of the CPU, which is directly attached to the machine’s heatsink, functions to pull out the hot air coming from the fins of the heatsink. That is the reason why CPU fans are crucial in maintaining the CPU temperature and keeping it cool.
These fans are available in varied sizes in today’s market, and they include either aluminum and copper heatsink or just aluminum or copper heatsink. It is the specifications of a CPU fan that determines its width and the inclusion of ball bearings. A CPU fan that features ball bearings is usually much quieter compared to one without the ball bearings.
Again, the type of CPU fan along with the heatsink decides its compatibility with a CPU. That’s why it is important that you know what CPU you own before buying a CPU fan.
Also, you should learn which CPU is equipped with cooling options and which is not. Take the unlocked Intel processors, for example, which don’t provide CPU cooling. And, high-end CPUs like Ryzen don’t include a CPU fan.
Such premium quality processors need top-quality cooling solutions (aftermarket) for smooth and effective functioning. Again, a CPU that does not include a cooling option is usually designed to overclock, which makes it crucial to equip the CPU with a cooling feature.
Headers for CPU Fans
As mentioned earlier an important aspect of sys fan VS CPU fan is the difference between their headers. A header for the CPU fan connects the fan with the power pin. This header is made using 4 pins in general.
The power to the fan for the CPU is provided by this header, which is its main function. It also functions at 1A which is its max amp rating. There is usually only 1 header for the CPU fan secured to the motherboard.
A point to note here is that if the header of the CPU fan remains disconnected from the CPU fan, then your machine will not start.
FAQ
Is it possible for a personal computer to function if there is no sys fan?
Technically, it is possible because the machine build includes fans, which can either be allowed to function or disabled, allowing the computer to run without a fan working in it.
Is a CPU fan a must for a PC?
Probably, the answer is yes. However, if your machine’s CPU functions on low power, then a heatsink that is passive, will do the job. That’s because the heatsink works as a cooler for the CPU and maintains its temperature.
Is it possible to connect the sys fan with the header of a CPU fan?
Yes, it is possible to do so. Consider splitting the single header of the CPU fan with the help of a Y-splitter. Then connect the case fan and the fan for CPU cooling to that split header. It is not ideal but the configuration can help if your machine doesn’t get cooled properly.
What number of sys fan headers can be secured to a motherboard?
Several sys fan headers can be secured to a motherboard. The number varies from 2-3 and even more sometimes.
Is it possible for one header to allow the running of multiple fans?
It is definitely possible for a header to allow two or three fans to run. Most of the fans come with a 0.10 to 0.30 A rating, which makes it possible for these fans to run on one header.
Conclusion
Hopefully, these lines have given you a clear understanding regarding sys fan VS CPU fan, including the difference in their locations and functions. Such knowledge can help you greatly when you are trying to develop a proper and effective system for cooling your personal computer, and improving its overall efficiency.